-
 Comprehensive Insights into Sarcopenia in Dialysis Patients: Mechanisms, Assessment, and Therapeutic Approaches
Comprehensive Insights into Sarcopenia in Dialysis Patients: Mechanisms, Assessment, and Therapeutic Approaches -
 The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Obesity Risk Prediction and Management: Approaches, Insights, and Recommendations
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Obesity Risk Prediction and Management: Approaches, Insights, and Recommendations -
 Prognostic Differences Between Early-Onset and Late-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Prognostic Differences Between Early-Onset and Late-Onset Colorectal Cancer -
 Hypertension and Atrial Fibrillation: Bridging the Gap Between Mechanisms, Risk, and Therapy
Hypertension and Atrial Fibrillation: Bridging the Gap Between Mechanisms, Risk, and Therapy -
 Next-Generation Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Depression: Integrating Digital Tools, Teletherapy, and Personalization for Enhanced Mental Health Outcomes
Next-Generation Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Depression: Integrating Digital Tools, Teletherapy, and Personalization for Enhanced Mental Health Outcomes
Journal Description
Medicina
Medicina
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal that covers all problems related to medicine. The journal is owned by the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences (LUHS) and is published monthly online by MDPI. Partner organizations are the Lithuanian Medical Association, Vilnius University, Rīga Stradiņš University, the University of Latvia, and the University of Tartu.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2023)
Latest Articles
Predictors of Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal Bayesian Analysis
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 877; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050877 (registering DOI) - 11 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition that significantly affects cognitive, emotional, and functional abilities in older adults. This study aimed to explore how demographic, clinical, and psychological factors influence the progression of cognitive decline in patients diagnosed
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition that significantly affects cognitive, emotional, and functional abilities in older adults. This study aimed to explore how demographic, clinical, and psychological factors influence the progression of cognitive decline in patients diagnosed with AD. Materials and Methods: A total of 101 patients were evaluated retrospectively and followed longitudinally at three different time points, using standardized instruments, including the MMSE, Reisberg’s GDS, clock-drawing test, MADRS, and Hamilton depression scale. Statistical methods included non-parametric tests, mixed-effect modeling, and Bayesian analysis. Results: Most patients were older women from rural areas, predominantly in moderate-to-severe stages of AD. Age showed a significant association with cognitive decline (p < 0.05), and depression—particularly in moderate and severe forms—was strongly linked to lower MMSE scores (p < 0.001). Over 70% of the participants had some degree of depression. The clock-drawing test highlighted visuospatial impairments, consistent with everyday functional loss. Although donepezil and memantine combinations appeared to be more frequently prescribed, no treatment showed a statistically significant advantage, and confidence interval overlaps suggest caution in interpreting differences between therapies. Longitudinal models confirmed a progressive and accelerated decline, with inter-individual variability becoming more pronounced in later stages. Although comorbidities, such as hypertension and diabetes, were frequent, they did not show a statistically significant effect on MMSE scores in this cohort. Conclusions: Age and depression appear to play central roles in the pace of cognitive deterioration in AD. Given the limited efficacy of most current therapies, these findings highlight the need for earlier intervention and a more personalized, integrated approach—combining cognitive care, psychiatric support, and comorbidity management—to better meet the needs of patients with AD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurology)
Open AccessArticle
Observational Study on Progressive Muscle Relaxation and Breathing Control for Reducing Dental Anxiety in Children
by
Sorana Maria Bucur, Ioana Maria Crișan, Dorin Ioan Cocoș, Eugen Silviu Bud and Carmen Galea
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 876; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050876 (registering DOI) - 10 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Dental anxiety is a common barrier to pediatric oral care. Non-pharmacological relaxation techniques like Jacobson’s Progressive Muscle Relaxation (JPMR) and Breathing Control (BC) may help reduce psychological and physiological stress. This study assessed the utility of JPMR and BC
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Dental anxiety is a common barrier to pediatric oral care. Non-pharmacological relaxation techniques like Jacobson’s Progressive Muscle Relaxation (JPMR) and Breathing Control (BC) may help reduce psychological and physiological stress. This study assessed the utility of JPMR and BC in reducing dental anxiety and physiological arousal in children and adolescents. Materials and Methods: In this observational study, 189 participants aged 8–17 undergoing non-invasive dental procedures were assigned to JPMR (n = 63), BC (n = 63), or control (n = 63) groups. Dental anxiety was measured with the Romanian-validated IDAF-4C+, and physiological stress was measured via blood pressure and heart rate. Pre and post-intervention data were analyzed using paired t-tests, ANOVA, and cluster analysis. Results: JPMR led to the highest reductions in IDAF-4C+ scores (Δ = −1.23, p < 0.001, d = 1.12) and systolic blood pressure (Δ = −9.4 mmHg, p < 0.01). BC showed moderate anxiety reduction (Δ = −0.64, p < 0.05, d = 0.61) with minor physiological changes. The control group showed no significant change. Cluster analysis revealed three response patterns: (1) high anxiety–strong responders (n = 58), mainly benefiting from JPMR; (2) moderate anxiety–partial responders (n = 74); and (3) low anxiety–non-responders (n = 57). Younger age and female gender were linked to better JPMR response. Conclusions: JPMR is an effective and practical method for reducing dental anxiety and physiological stress in pediatric dental care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Dentistry and Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
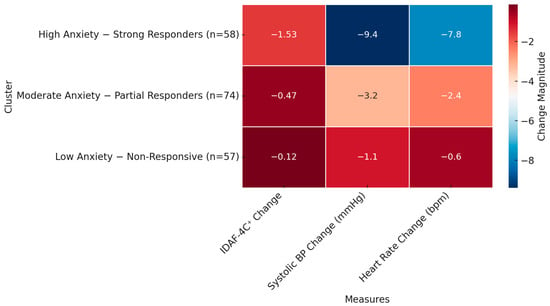
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging with Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Nonischemic Cardiomyopathies: An In-Depth Review of Techniques and Clinical Applications
by
Ilir Sharka, Giorgia Panichella, Chrysanthos Grigoratos, Matilda Muca, Carmelo De Gori, Petra Keilberg, Giovanni Novani, Valerio Barra, Hana Hlavata, Matteo Bianchi, Denisa Simona Zai, Francesca Frijia, Alberto Clemente, Giancarlo Todiere and Andrea Barison
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 875; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050875 (registering DOI) - 10 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Nonischemic cardiomyopathies comprise a wide spectrum of heart muscle disorders characterized by different morphological, functional, and tissue abnormalities. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) represents the gold standard imaging modality for assessing cardiac morphology, systolic function, and tissue characterization, thereby aiding
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Nonischemic cardiomyopathies comprise a wide spectrum of heart muscle disorders characterized by different morphological, functional, and tissue abnormalities. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) represents the gold standard imaging modality for assessing cardiac morphology, systolic function, and tissue characterization, thereby aiding in early diagnosis, precise phenotyping, and tailored treatment. The aim of this review is to provide an up-to-date overview of CMR techniques for studying myocardial perfusion and their applications to nonischemic cardiomyopathy, not only to rule out an underlying ischemic aetiology but also to investigate the pathophysiological characteristics of microcirculatory dysfunction in these patients. Materials and Methods: We performed a structured review of the literature focusing on first-pass gadolinium perfusion sequences, stress protocols, and emerging pixel-wise perfusion mapping approaches. Studies were selected to illustrate the methods for image acquisition, post-processing, and quantification of myocardial blood flow (MBF) and myocardial perfusion reserve (MPR), as well as to highlight associations with clinical endpoints. Results: First-pass CMR perfusion imaging reliably detects diffuse and regional microvascular dysfunction across cardiomyopathies. Semi-quantitative parameters (e.g., upslope, MPRI) and quantitative MBF mapping (mL/g/min) have demonstrated that impaired perfusion correlates with disease severity, extent of fibrosis, and adverse outcomes, including heart failure hospitalization, arrhythmias, and mortality. Novel automated pixel-wise mapping enhances reproducibility and diagnostic accuracy, distinguishing coronary microvascular dysfunction from balanced three-vessel disease. Microvascular dysfunction—present in approximately 50–60% of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), 40–80% of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), and >95% of cardiac amyloidosis (CA) patients—has emerged as a key driver of adverse outcomes. Perfusion defects appear early, often preceding overt hypertrophy or fibrosis, and provide incremental prognostic value beyond conventional CMR metrics. Conclusions: CMR represents a powerful tool for detecting myocardial perfusion abnormalities in nonischemic cardiomyopathies, improving phenotyping, risk stratification, and personalized management. Further standardization of quantitative perfusion techniques will facilitate broader clinical adoption.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Imaging Techniques in Myocardial Ischemia: Current Applications and Future Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures
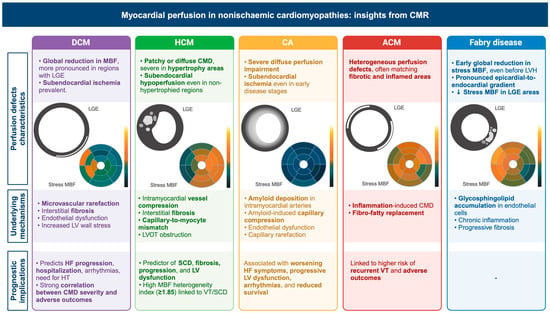
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Endodontic Outcomes with the Synergistic Microbicidal and Activated Root-Cleansing Technique (SMART): A Novel Approach to Root Canal Irrigation
by
Max Foroughi, Sara Abolmaali, Hamid Abedi and Theodore Ravenel
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 874; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050874 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Successful endodontic treatment requires thorough disinfection and removal of the smear layer to prevent reinfection. However, conventional irrigants like sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) can compromise dentin integrity. This study assessed the efficacy of the Synergistic Microbicidal and
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Successful endodontic treatment requires thorough disinfection and removal of the smear layer to prevent reinfection. However, conventional irrigants like sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) can compromise dentin integrity. This study assessed the efficacy of the Synergistic Microbicidal and Ablative Root canal Technique (SMART), which integrates AromaRoot, a biocompatible irrigation solution based on quaternary ammonium compounds, with 980 nm diode laser activation, to enhance bacterial reduction and smear layer removal. Materials and Methods: Sixty extracted single-rooted human teeth were inoculated with Enterococcus faecalis and divided into four treatment groups using NaOCl, AromaRoot, and 980 nm laser, either alone or in combination. Bacterial counts were measured as colony-forming units per milliliter (CFU/mL). For smear layer analysis, 56 extracted teeth were prepared and irrigated using EDTA, AromaRoot, and laser activation, followed by scanning electron microscopy to evaluate dentinal tubule exposure. Data were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis and ANOVA. Results: The combination of AromaRoot, NaOCl, and laser activation achieved a 99.00% bacterial reduction (from 8082 to 60 CFU/mL, p < 0.001), outperforming NaOCl alone (98.34%, 131 CFU/mL). For smear layer removal, AromaRoot with laser achieved 78.5% open dentinal tubules in the apical third, significantly higher than EDTA alone (64.5%, p < 0.05), though EDTA remained superior in the coronal third (89.0% vs. 81.0%, p > 0.05). Conclusions: The SMART technique significantly improves both disinfection and smear layer removal in root canal therapy, particularly in the apical region. These findings suggest that AromaRoot, especially when laser-activated, may serve as a safe and effective alternative to conventional irrigants, warranting further clinical evaluation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Research on Endodontic Therapy)
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness of Combined Whole-Body Vibration and Intensive Therapeutic Exercise on Functional Capacity in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
by
Iñigo Monzón-Tobalina, Rosa María Ortiz-Gutiérrez, Ángela Concepción Álvarez-Melcón, Álvaro Pérez-Somarriba, Patricia Martín-Casas and María José Díaz-Arribas
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 873; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050873 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Whole-body vibration (WBV) therapy presents controversial evidence regarding its effectiveness in improving lower limb functional capacity in children with cerebral palsy (CP), particularly when applied continuously as an adjunct to a physiotherapy program with demonstrated efficacy. This study aimed to
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Whole-body vibration (WBV) therapy presents controversial evidence regarding its effectiveness in improving lower limb functional capacity in children with cerebral palsy (CP), particularly when applied continuously as an adjunct to a physiotherapy program with demonstrated efficacy. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of adding WBV to an intensive therapeutic exercise and functional training program in improving lower limb functional capacity in children with spastic CP. Materials and Methods: Thirty children with spastic CP were randomly assigned to a control or experimental group. Both groups completed a 4-week intensive therapeutic exercise and functional training program (4 sessions/week). The experimental group additionally received daily WBV. Results: Both groups showed significant improvements in all analysed variables at 1, 2, and 6 months post-treatment (p < 0.001). However, no significant between-group differences were found for primary (GMFM-88 D: p = 0.80; GMFM-88 E: p = 0.91) or secondary outcomes in relation to muscle tone and strength, and balance. A trend toward greater improvement was observed in the experimental group but without statistical significance. Conclusions: The addition of WBV to an intensive program of therapeutic exercise and functional training does not yield additional benefits in motor function, spasticity, gait capacity, lower limb muscle strength, or balance compared to intensive physiotherapy and functional training alone in children with spastic CP. The significant within-group improvements can be attributed to the intensive physiotherapy intervention, comprising therapeutic exercises and functional training.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Exercise-Induced Neurogenesis, Neuronal and Functional Adaptations in Neurorehabilitation)
►▼
Show Figures
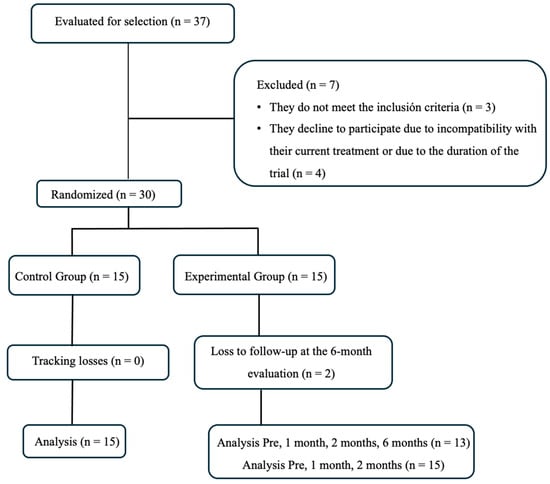
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of the Effectiveness of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (taVNS) and Vestibular Rehabilitation in Patients with Unilateral Vestibular Hypofunction
by
Tuğba Türk Kalkan, Devrim Tarakçi, Gamze Kiliç and Cengiz Çelikyurt
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 872; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050872 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a frequently used neuromodulation method in recent years. While the mechanism of improvement in diseases such as epilepsy, dementia, and depression is being studied, its potential effect on vestibular dysfunction is also being investigated. The aim
[...] Read more.
Background: Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a frequently used neuromodulation method in recent years. While the mechanism of improvement in diseases such as epilepsy, dementia, and depression is being studied, its potential effect on vestibular dysfunction is also being investigated. The aim of our study was to investigate the effect of transcutaneous auricular VNS (taVNS) on the vestibular symptoms of unilateral vestibular hypofunction (UVH). Methods: Forty patients diagnosed with UVH were randomly divided into two groups. Group 1 received vestibular rehabilitation. Group 2 received taVNS and vestibular rehabilitation. Both groups received treatment one day a week for eight weeks. Before and after the treatment, balance of the participants was assessed with modified-CTSIB (m-CTSIB), limit of stability (LOS), Tandem and One-Leg Stance (OLS) tests; visual acuity was assessed with dynamic visual acuity (DVA), dizziness severity, and fatigue severity with a visual analog scale (VAS); kinesiophobia was assessed with the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK); depression and anxiety was assessed with the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS); and quality of life was assessed with the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI). Results: At the end of eight weeks, patients in Group 2 showed significantly greater improvement in balance, dizziness, fatigue, kinesiophobia, anxiety, and depression. There was no significant difference in visual acuity and quality of life between the groups. Conclusions: The positive effects of taVNS on vestibular symptoms have been observed. As a new approach, taVNS can be included in the treatment of patients with UVH in addition to vestibular rehabilitation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurology)
►▼
Show Figures
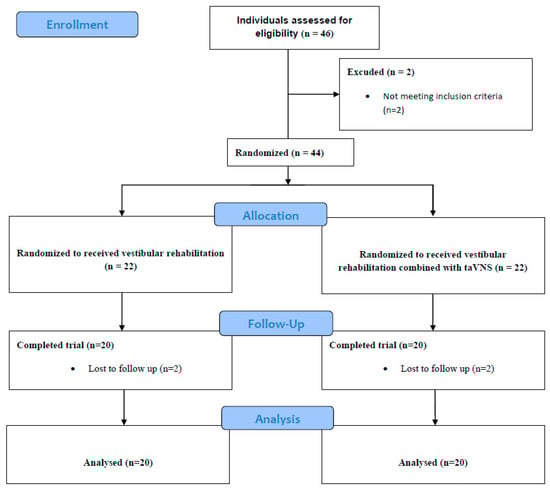
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Dexamethasone on Three-Dimensional Stem Cell Spheroids: Morphology, Viability, Osteogenic Differentiation
by
Heera Lee, Ju-Hwan Kim, Hyun-Jin Lee and Jun-Beom Park
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 871; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050871 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Dexamethasone has been widely researched for its ability to promote osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells in basic research. This study focused on examining the effects of dexamethasone on both cell viability and osteogenic differentiation in three-dimensional stem cell
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Dexamethasone has been widely researched for its ability to promote osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells in basic research. This study focused on examining the effects of dexamethasone on both cell viability and osteogenic differentiation in three-dimensional stem cell spheroids. Materials and Methods: These spheroids were created using concave microwells and exposed to dexamethasone at concentrations ranging from 0 μM to 100 μM, including intermediate levels of 0.1 μM, 1 μM, and 10 μM. Microscopic analysis was used to qualitatively assess cellular viability, while a water-soluble tetrazolium salt-based assay provided quantitative viability data. Osteogenic differentiation was evaluated by measuring alkaline phosphatase activity and calcium deposition using Alizarin Red staining. Additionally, the expression levels of genes associated with osteogenesis were measured through quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Results: The spheroids successfully self-assembled within the first 24 h and maintained their structural integrity over a seven-day period. Analysis of cell viability showed no statistically significant differences across the various dexamethasone concentrations tested. Although there was an observed increase in alkaline phosphatase activity and calcium deposition following dexamethasone treatment, these differences were not statistically significant. RUNX2 gene expression was upregulated in the 1 μM, 10 μM, and 100 μM groups, while COL1A1 expression significantly increased at 0.1 μM and 1 μM. Conclusions: These results indicate that dexamethasone supports cell viability and enhances RUNX2 and COL1A1 expression in stem cell spheroids.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Dentistry and Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
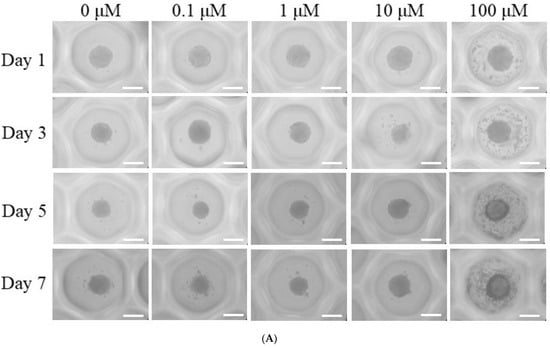
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurements in Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery with Pulsatile and Non-Pulsatile Flow
by
Leyla Kazancıoğlu and Şule Batçık
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 870; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050870 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: In coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgeries, monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) is crucial due to neurological risks. Although pulsatile flow (PF) during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is considered more physiological than non-pulsatile flow (NPF), its impact on ICP remains unclear. This
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: In coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgeries, monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) is crucial due to neurological risks. Although pulsatile flow (PF) during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is considered more physiological than non-pulsatile flow (NPF), its impact on ICP remains unclear. This study aimed to compare preoperative and postoperative optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) measurements between PF and NPF techniques to evaluate their effect on ICP changes. Materials and Methods: Sixty patients undergoing elective CABG (aged 45–75 years, ASA II-III-IV) were enrolled and divided into two groups depending on the cardiopulmonary bypass technique determined by the surgeon: PF (Group P, n = 30) and NPF (Group NP, n = 30). ONSD measurements were performed with ultrasound before surgery (Tpreop) and after surgery (Tpostop). Hemodynamic parameters and jugular and carotid vessel diameters were also recorded. Statistical analysis included t-tests, Mann–Whitney U-tests, chi-square tests, and Pearson correlation. Results: Both groups demonstrated significant increases in ONSD postoperatively compared to preoperative values (p < 0.001). However, no statistically significant difference in the magnitude of ONSD change was observed between the PF and NPF groups (p > 0.05). Group P showed lower ejection fractions and higher total inotrope requirements compared to Group NP (p < 0.01), but these factors did not translate into differences in postoperative ICP dynamics. Conclusions: ONSD measurements increased significantly after CABG surgery, regardless of perfusion type. PF and NPF strategies were comparable in terms of their effects on ICP as reflected by ONSD changes. ONSD ultrasonography appears to be a simple, rapid, and non-invasive tool for perioperative ICP monitoring in cardiac surgery. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings with dynamic intraoperative monitoring and neurocognitive assessments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Intensive Care/ Anesthesiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Demographic and Clinical Determinants of Conjugated Pneumococcal Vaccine Uptake and Short-Term All-Cause Mortality in Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Cohorts in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Prospective Cohort Study
by
Yalçın Velibey, Erkan Kahraman, Melih Oz, Murat Gokalp, Kader Ozturk, Muhsin Melik, Utku Ulukoksal, Ufuk Egemen Yazar, Furkan Fatih Yucedag, Elif Ozoguz, Emre Ozguclu, Mutlu Seyda Ocalmaz, Mehmet Eren, Osman Bolca and Tolga Sinan Güvenç
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 869; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050869 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Patients with heart failure (HF) are at risk of increased morbidity and mortality related to pneumococcal pneumonia, and routine vaccination with a conjugated pneumococcal vaccine (PCV) for HF patients is strongly endorsed by all major international guidelines. Despite this,
[...] Read more.
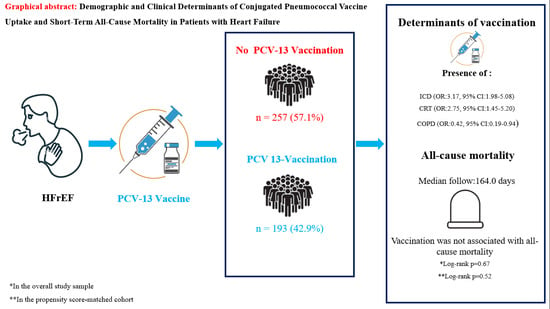
Background and Objectives: Patients with heart failure (HF) are at risk of increased morbidity and mortality related to pneumococcal pneumonia, and routine vaccination with a conjugated pneumococcal vaccine (PCV) for HF patients is strongly endorsed by all major international guidelines. Despite this, data on the factors associated with vaccine uptake remain scarce. The aim of this study was to understand the demographic and clinical factors associated with vaccine uptake in patients with HF and analyze the all-cause mortality in the vaccinated and unvaccinated cohorts. Materials and Methods: Four hundred and fifty patients with HF and a reduced ejection fraction followed up at a single center were enrolled. Patients were followed up for a median of 164.0 (148.0–181.0) days. Results: In total, 193 of the 450 patients (42.9%) were vaccinated with PCV-13 at enrollment. Vaccinated patients were more likely to have an implantable device, namely an implantable cardioverter/defibrillator (ICD), cardiac resynchronization treatment (CRT) or left ventricular assist device (LVAD), and less likely to have a past medical history of hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at baseline. After multivariable adjustment, the presence of an ICD (OR: 3.17, 95% CI: 1.98–5.08), CRT (OR: 2.75, 95% CI: 1.45–5.20) and COPD (OR: 0.42, 95% CI: 0.19–0.94) remained as determinants of vaccination. All-cause mortality was not different across vaccinated or unvaccinated patients either in the unmatched (log-rank p = 0.67) or matched (log-rank p = 0.52) cohorts. Conclusions: The presence of implantable devices and coexisting COPD was associated with a higher and lower likelihood of vaccination with PCV-13, respectively. No difference in mortality across cohorts was observed in this observational analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Spousal Support and Stress Coping Styles of Pregnant Women Diagnosed with Fetal Anomaly
by
Sevim Tuncer Can, Sevler Yıldız, Ceren Sağlam, Hakan Golbasi and Atalay Ekin
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 868; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050868 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Pregnant women may experience various difficulties when abnormal conditions are detected in their babies. We examined the relationship between anxiety and depression levels, spousal support, and stress-coping styles in pregnant women diagnosed with fetal anomalies. Materials and Methods: A
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Pregnant women may experience various difficulties when abnormal conditions are detected in their babies. We examined the relationship between anxiety and depression levels, spousal support, and stress-coping styles in pregnant women diagnosed with fetal anomalies. Materials and Methods: A total of 157 pregnant women, 59 of whom were diagnosed with fetal anomalies and 98 of whom were healthy with no obstetric complications, were included in this study. All participants were administered the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Spousal Support Scale (SSS), and Coping Styles Scale (CSS) questionnaires. The data were compared statistically. Results: The BAI (p < 0.001) and the Submissive Approach (p = 0.004), which is a subdimension of the CSS, were significantly higher in the group of pregnant women diagnosed with fetal anomalies than in the control group. Multivariate logistic regression analysis performed to calculate the risk of fetal anomalies showed that having a high school education or below and living in the city were associated with a higher risk of fetal anomaly than living in the countryside. The cut-off value of 4 for the BAI had a sensitivity of 64.4% and a specificity of 65.3. Additionally, a cut-off value of 6 for the Submissive Approach, a CSS subdimension, had a 66.1% sensitivity and a 57.1% specificity. A significant negative correlation was observed between the Spousal Support Scale, the BDI, and the gravidity in the case group. There was a positive correlation between the BAI and the BDI and a significant negative correlation between the BAI and these CSS subdimensions: Self-Confident Approach, Seeking Social Support, and Optimistic Approach. There was a positive correlation between the BDI and the Helpless Approach subdimension of the CSS and a significant negative correlation between the BDI and the Self-Confident Approach and Optimistic Approach subdimensions, as well as the gestational age at which fetal anomaly was detected. A significant positive correlation was observed between the BDI and the Helpless Approach subdimension of the CSS, while significant negative correlations were observed between the BDI and the Self-Confident Approach and Optimistic Approach subdimensions and the gestational age at which the fetal anomaly was detected. Conclusions: The pregnant women diagnosed with fetal anomalies experienced anxiety, but most tended to use the submissive coping style to deal with stress, and their partners also supported them.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Obstetrics and Gynecology)
►▼
Show Figures
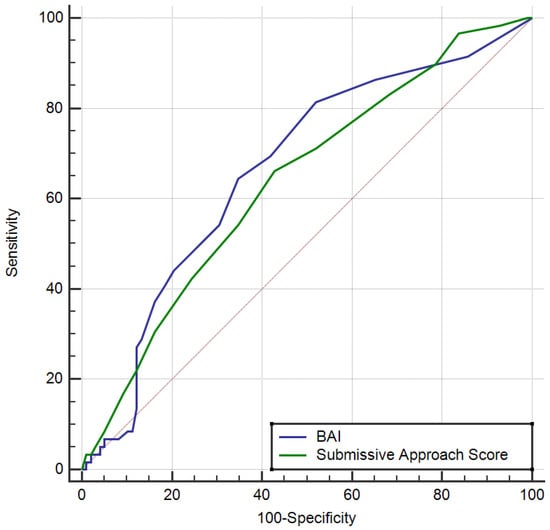
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prognostic Value of B7-H3 and a Novel Scoring System in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma
by
Faruk Recep Özalp, Kutsal Yörükoğlu, Eda Çalışkan Yıldırım, Mehmet Uzun, Erkut Demirciler and Hüseyin Salih Semiz
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 867; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050867 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a biologically heterogeneous malignancy, and traditional prognostic models often fail to provide accurate risk stratification. B7-H3 (CD276), an immune checkpoint molecule, has been implicated in RCC progression but remains underexplored as a prognostic biomarker.
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a biologically heterogeneous malignancy, and traditional prognostic models often fail to provide accurate risk stratification. B7-H3 (CD276), an immune checkpoint molecule, has been implicated in RCC progression but remains underexplored as a prognostic biomarker. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 52 patients with localized RCC who underwent nephrectomy. Immunohistochemical staining was used to assess B7-H3 expression. A novel prognostic scoring system, the Renal Immune Prognostic Index (RIPI), incorporating B7-H3 expression, tumor necrosis, tumor grade, and pathological staging, was developed and validated. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard models were employed to evaluate disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). Results: High B7-H3 expression was significantly associated with shorter DFS (12 vs. 54 months; p = 0.001) and OS (70 vs. 123 months; p = 0.002). The RIPI demonstrated strong prognostic performance, stratifying the patients into distinct risk groups with a C-index of 0.82. The high-risk patients had a median DFS of 14 months, compared with 125 months in the low-risk group (p < 0.001). Conclusions: B7-H3 expression serves as a significant prognostic biomarker in localized RCC, correlating with poorer survival outcomes. The integration of B7-H3 into the RIPI enhances risk stratification by incorporating both molecular and pathological features. These findings support the incorporation of immune biomarkers into clinical practice and highlight B7-H3 as a potential target for novel therapeutic strategies in RCC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Genetic Patterns Related with the Development and Progression of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review
by
Andreea-Dalila Nedelcu, Andreea-Bianca Uzun, Viorela-Mihaela Ciortea, Laszlo Irsay, Liliana-Elena Stanciu, Dan Marcel Iliescu, Florina Ligia Popa and Mădălina-Gabriela Iliescu
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 866; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050866 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Despite their high prevalence, sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity remain underdiagnosed worldwide, significantly impacting the health and quality of life of aging individuals. Due to their multifactorial nature, the current management strategies do not address their underlying pathogenesis. This systematic review
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Despite their high prevalence, sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity remain underdiagnosed worldwide, significantly impacting the health and quality of life of aging individuals. Due to their multifactorial nature, the current management strategies do not address their underlying pathogenesis. This systematic review aims to identify single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with sarcopenia and/or sarcopenic obesity in humans. Materials and Methods. This systematic literature review followed the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)” guidelines and the protocol registered in PROSPERO. Extensive research was performed in six databases (PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and SpringerLink) using keywords such as “sarcopenia”, “sarcopenic obesity”, “single nucleotide polymorphisms”, “SNPs”, and “genetic variants”. The Q-Genie and ROBINS-E tools were utilized to assess the quality of the included studies. Results: The final analysis included 12 studies, which were classified as good-quality according to the Q-Genie assessment and indicated a low to moderate risk of bias according to the ROBINS-E evaluation, collectively identifying 43 SNPs significantly associated with sarcopenia or sarcopenic obesity. Specifically, 24 SNPs were linked to sarcopenia, while 19 were associated with sarcopenic obesity. Conclusions: Understanding the implications of SNPs provides valuable insights into individual susceptibility and the variability observed across populations, potentially leading to more targeted and effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. Advancing clinical practice requires ongoing research into the genetic aspects of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases and Health Promotion)
►▼
Show Figures
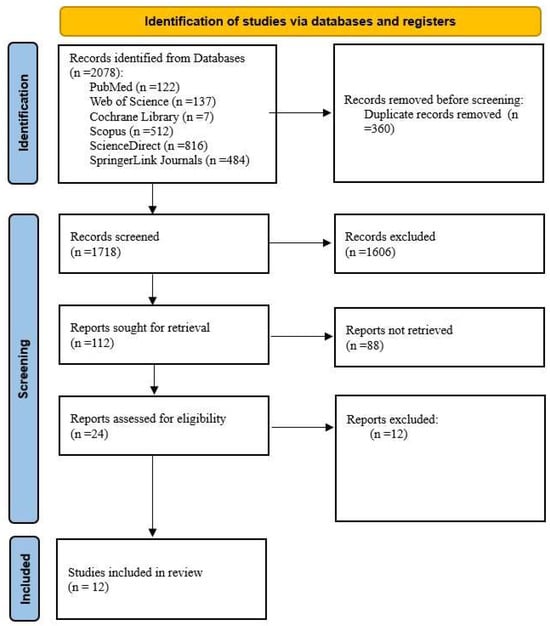
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Pre-Treatment Inflammatory Biomarkers in Predicting Tumor Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Rectal Cancer
by
Yunus Emre Altıntaş, Ahmet Bilici, Özcan Yıldız, Oğuzcan Kınıkoğlu and Ömer Fatih Ölmez
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 865; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050865 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the predictive and prognostic value of pre-treatment systemic inflammatory markers in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (RC) undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) or radiotherapy (RT) alone. Materials and Methods: A total of 79
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the predictive and prognostic value of pre-treatment systemic inflammatory markers in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (RC) undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) or radiotherapy (RT) alone. Materials and Methods: A total of 79 patients with biopsy-confirmed locally advanced RC treated at a single tertiary center between 2011 and 2017 were retrospectively analyzed. Pre-treatment blood-based inflammatory indices, including neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), derived NLR, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), and hemoglobin levels, were recorded. Tumor response was assessed using the Ryan tumor regression grade (TRG), and associations between laboratory parameters, treatment response, and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were evaluated. Results: Among 79 patients (mean age: 55.9 ± 11.98 years; 67.1% male), 57 received neoadjuvant CRT and 22 underwent short-course RT. Complete pathological response (pCR) was observed in 10 patients (12.7%). No statistically significant associations were found between baseline inflammatory markers and TRG, tumor differentiation, or pCR. ROC analysis revealed that none of the markers demonstrated significant discriminatory power for predicting tumor response or recurrence. However, a weak but statistically significant inverse correlation was identified between poor TRG response and higher baseline values of NLR, derived NLR, and PLR (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Inflammatory biomarkers such as NLR, PLR, and LMR, while easily accessible and cost-effective, did not demonstrate strong predictive or prognostic value in this cohort of RC patients receiving neoadjuvant therapy. These findings suggest that reliance solely on systemic inflammatory indices may be insufficient for predicting treatment outcomes, emphasizing the need for integrative models incorporating molecular and pathological markers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
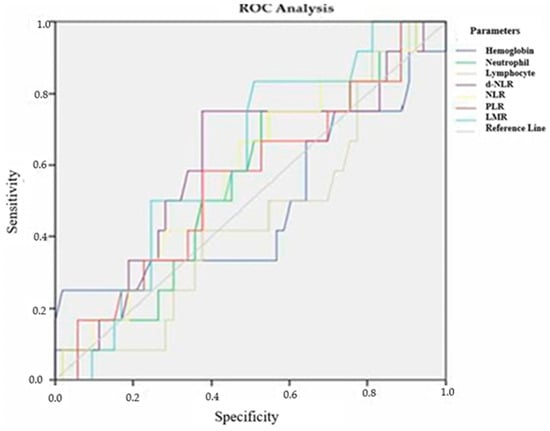
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sepsis Burden in a Major Romanian Emergency Center—An 18-Year Retrospective Analysis of Mortality and Risk Factors
by
Florentina Mușat, Dan Nicolae Păduraru, Alexandra Bolocan, Cosmin-Alexandru Palcău, Andrei-Alexandru Bunea, Daniel Ion and Octavian Andronic
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 864; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050864 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Sepsis is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, yet data from Central and Eastern Europe remain scarce. Our study aims to address the scarcity of information regarding the characteristics and mortality rates of patients with sepsis by reporting
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Sepsis is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, yet data from Central and Eastern Europe remain scarce. Our study aims to address the scarcity of information regarding the characteristics and mortality rates of patients with sepsis by reporting recent data from one of the largest emergency centers in Romania over an 18-year period (2007–2024). Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 12,089 adult patients diagnosed with sepsis at the University Emergency Hospital of Bucharest. Patients were identified using International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) codes and free-text diagnosis. Demographic and clinical data were extracted, including comorbidities, interventions, and mortality outcomes. Associations between comorbidities and in-hospital mortality were assessed using odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: The study population had a mean age of 68.7 years, with a slight predominance of males (50.9%). In-hospital mortality was 53.9%, and 30-day mortality reached 85.1%. The most common comorbidities were diabetes (27.2%), chronic kidney disease (14.0%), and cancer (12.9%). Pneumonia (OR = 2.08, 95% CI: 1.89–2.28), cirrhosis (OR = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.40–2.03), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (OR = 1.50, 95% CI: 1.27–1.77) were strong predictors of mortality, while diabetes was associated with a slightly lower risk (OR = 0.90, 95% CI: 0.83–0.97). Conclusions: Sepsis-related mortality in Romania is higher than reported in Western Europe and North America, resembling trends in resource-limited settings. Targeted early recognition, antimicrobial stewardship, and improved intensive care units (ICU) resource allocation are crucial for reducing mortality. Multicenter studies and microbiological analyses are needed to further understand sepsis outcomes in this region.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Global Perspectives on Sepsis: Epidemiology, Awareness and Treatment Strategies)
►▼
Show Figures
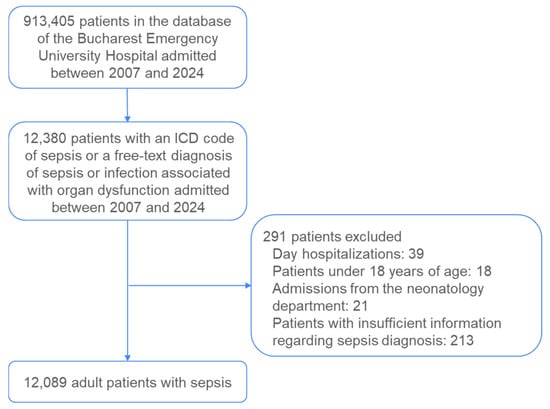
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Early Postoperative Increase in Transforming Growth Factor Beta-1 Predicts Microvascular Flap Loss in Reconstructive Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study
by
Rihards Peteris Rocans, Janis Zarins, Evita Bine, Insana Mahauri, Renars Deksnis, Margarita Citovica, Simona Donina, Sabine Gravelsina, Anda Vilmane, Santa Rasa-Dzelzkaleja, Olegs Sabelnikovs and Biruta Mamaja
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 863; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050863 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Microvascular flap surgery is a widely used reconstructive technique for the repair of various defects. Biomarkers have become an essential tool for monitoring flap viability, early detection of complications, and prediction of surgical outcomes. Studies focusing on immunomodulatory cytokines in
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Microvascular flap surgery is a widely used reconstructive technique for the repair of various defects. Biomarkers have become an essential tool for monitoring flap viability, early detection of complications, and prediction of surgical outcomes. Studies focusing on immunomodulatory cytokines in the early prediction of microvascular flap complications are lacking. We aimed to investigate the predictive value of postoperative changes in transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1) for microvascular flap complications. Materials and Methods: This prospective observational study comprised 44 adults scheduled for elective microvascular flap surgery. Preoperative blood samples for analysis were obtained before surgery, prior to the administration of intravenous fluids. Postoperative blood draws were collected after surgery, before leaving the operating room. Preoperative and postoperative serum concentrations of TGF-β1, as well as preoperative plasma albumin, total protein, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, full blood count, albumin, interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and fibrinogen, were determined. Results: Postoperative changes in TGF-β1 were higher in cases with flap loss compared to patients with healthy recovery or patients with minor flap complications (0.403 log10 of ng/mL [0.024–0.782] vs. 0.157 [0.029–0.285] vs. −0.089 [−0.233–0.056], p = 0.002). Increased postoperative TGF-β1 was positively linked to preoperative C-reactive protein (p = 0.021), fibrinogen (p = 0.020), hematocrit (p = 0.039), and hemoglobin (p = 0.009). Conclusions: The postoperative increase in circulating TGF-β1 was associated with microvascular flap complications. Assessment of the postoperative changes in circulating TGF-β1 may be valuable for the early postoperative prediction of true flap loss.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights into Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
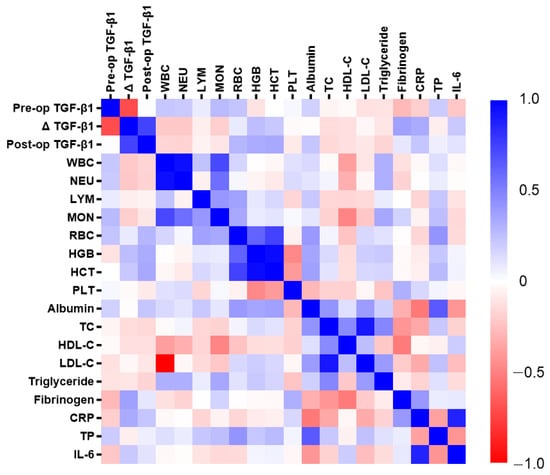
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Anxiety Levels and Physical Activity Among the Population of Saudi Arabia
by
Anwar A. Sayed, Ghaida Ghassan Alsisi, Amjad Faisal Aljohani, Manal Salman Aloufi, Samiyah Saleh Alhejaili and Reem Mebrek Almatrafi
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 862; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050862 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Anxiety is widely recognized as a common mental health issue. Extensive research highlights the benefits of adopting healthier lifestyle habits in improving both physical and mental wellbeing. This study aims to assess the levels of anxiety and physical activity,
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Anxiety is widely recognized as a common mental health issue. Extensive research highlights the benefits of adopting healthier lifestyle habits in improving both physical and mental wellbeing. This study aims to assess the levels of anxiety and physical activity, and if associations exist, among the population of Saudi Arabia. Materials and Methods: The study included a sample of 244 participants, who responded to an online survey containing demographic information, the Arabic versions of the General Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7), and the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ) as assessment tools. Results: The study participants had a median age of 31 years and most of them were females (64.7%). Almost three quarters of the participants had received a higher education (73.5%) and were nonsmokers (94.1%). Assessing their physical activity levels, moderate or low-intensity physical activities, particularly walking and cycling, were common. Participants’ anxiety levels, measured by the GAD-7, were higher in females, students, and employees. Physical activity, especially walking or cycling, was linked to lower anxiety, while sedentary behavior, characterized by less than three hours of daily activity, was also associated with reduced anxiety. Interestingly, the duration of physical activity had no significant impact on anxiety levels. Conclusions: This study examined how lifestyle factors, including physical activity and sedentary behavior, influence anxiety levels among a cohort in Saudi Arabia. It emphasizes the need to encourage moderate-intensity activities and limit sedentary time, especially among high-risk groups, like students and women, to help alleviate anxiety.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Psychiatry)
►▼
Show Figures
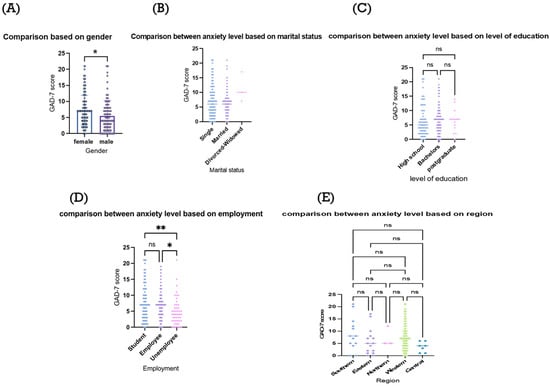
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Exploring the Link Between Vitamin K and Depression: A Systematic Review
by
Mohamad Hisham Hashim, Nik Nasihah Nik Ramli, Siti Nur Atiqah Zulaikah Nasarudin, Maisarah Abdul Mutalib, Muhammad Najib Mohamad Alwi, Aswir Abd Rashed and Rajesh Ramasamy
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 861; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050861 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Depression is a multifactorial mental health disorder involving inflammation, oxidative stress, neuroplasticity deficits, and metabolic dysfunction. Emerging research suggests that vitamin K, beyond its classical roles in coagulation and bone metabolism, may influence neurobiological processes relevant to mood regulation. This
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Depression is a multifactorial mental health disorder involving inflammation, oxidative stress, neuroplasticity deficits, and metabolic dysfunction. Emerging research suggests that vitamin K, beyond its classical roles in coagulation and bone metabolism, may influence neurobiological processes relevant to mood regulation. This systematic review evaluates the association between vitamin K and depressive symptoms and explores potential underlying mechanisms. Materials and Methods: A systematic search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, following PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Eligible studies included human or animal research examining associations between vitamin K status (dietary intake or serum levels) and depression-related outcomes. Fourteen studies met the inclusion criteria: eleven observational studies, one randomized controlled trial (RCT), and two preclinical animal studies. Results: Most observational studies reported an inverse association between vitamin K intake or serum levels and depressive symptoms across diverse populations. One small RCT demonstrated modest improvements in depression scores following vitamin K2 (menaquinone-7) supplementation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Two preclinical studies using non-depression models reported behavioral improvements and reduced oxidative stress following vitamin K2 administration. Conclusions: While preliminary findings suggest a potential role for vitamin K in pathways relevant to depression, the current evidence is limited by cross-sectional designs, lack of isoform-specific analyses, and the absence of depression-focused preclinical models. Mechanisms including inflammation reduction, oxidative stress modulation, sphingolipid regulation, and vitamin K-dependent protein signaling (e.g., GAS6 and osteocalcin) were discussed based on indirect evidence and require further investigation in depression-specific contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Western Experience of Hepatolithiasis: Clinical Insights from a Case Series in a Tertiary Center
by
Natale Calomino, Ludovico Carbone, Engjell Kelmendi, Stefania Angela Piccioni, Gianmario Edoardo Poto, Giulio Bagnacci, Luca Resca, Annalisa Guarracino, Sergio Tripodi, Bina Barbato, Stefano Brillanti, Franco Roviello, Gian Luigi Adani and Daniele Marrelli
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 860; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050860 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Objectives: Hepatolithiasis (HL), or intrahepatic bile duct stone disease, shows regional variation and is a rare condition in Western countries. While cases from East Asia are often linked to chronic biliary infections and brown pigment stones, Western HL more frequently
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Hepatolithiasis (HL), or intrahepatic bile duct stone disease, shows regional variation and is a rare condition in Western countries. While cases from East Asia are often linked to chronic biliary infections and brown pigment stones, Western HL more frequently involves cholesterol or black pigment stones, typically in the context of prior cholecystectomy, biliary interventions, or congenital anomalies. The disease is generally associated with significant morbidity, including recurrent cholangitis, biliary strictures, and risk of cholangiocarcinoma. This study aimed to characterize HL disease in an Italian case series. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 1450 patients with biliary stone disease treated between 2010 and 2024. HL was diagnosed in 14 patients (0.96%). Clinical records, imaging (ultrasound, CT, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography—MRCP, cholangiography), bile cultures, and stone composition (categorized as cholesterol, brown pigment, black pigment, or mixed using FTIR/XRD) were analyzed. Results: Among the 14 patients (mean age: 60.1 years; 64.3% female), 71.4% presented with recurrent cholangitis, while 28.6% were asymptomatic. Stones were left-sided in 57.1%, right-sided in 21.4%, and bilateral in 21.4%. Stone composition was cholesterol/mixed in 50%, brown pigment in 35.7%, and black pigment in 14.3%. Risk factors for bile stasis were present in 71.4% of cases. Bile cultures (available in nine cases) were positive in 77.8%. MRCP was highly effective for diagnosis. Hepatectomy achieved complete resolution in 35.7% of patients with unilobar disease; endoscopic/percutaneous therapy had a 44.4% recurrence rate. Interestingly, no cholangiocarcinoma was observed over a median follow-up of 4.8 years. Conclusions: Western HL is a rare, heterogeneous disease with distinct features. Cholesterol-predominant, infection-negative cases suggest a metabolic or surgical etiology. Hepatectomy offers durable outcomes in unilobar disease. Advanced imaging (MRCP, cholangioscopy) and personalized strategies are key to effective management.
Full article
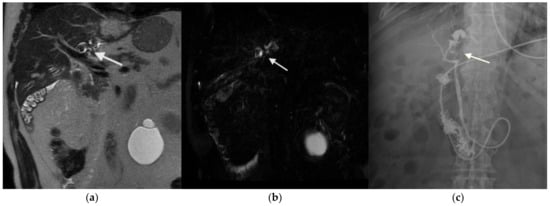
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Is Salvage Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation Still a Viable Treatment Option in Relapsed Myeloma Patients?
by
Luka Čemažar, Matevž Škerget and Barbara Skopec
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 859; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050859 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The role of salvage autologous stem cell transplantation (SAT) in relapsed multiple myeloma (MM) has been increasingly questioned, particularly with the emergence of novel immunotherapies and cellular therapies. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of SAT in a
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The role of salvage autologous stem cell transplantation (SAT) in relapsed multiple myeloma (MM) has been increasingly questioned, particularly with the emergence of novel immunotherapies and cellular therapies. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of SAT in a cohort of patients with relapsed MM following their first autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 78 patients from our institutional registry who underwent SAT for relapsed MM between April 2008 and October 2023. The primary endpoint was the progression-free survival (PFS), with secondary endpoints including the overall survival (OS) and overall response rates (ORRs) on day +100 after SAT. Results: The median age of the patients was 62 years (range: 48–78), and 32% were female. Most patients (81%) received reinduction therapy before SAT. The median PFS and OS from SAT were 24 months (95% CI: 20–36) and 76 months (95% CI: 48-NR), respectively. The ORR was 85%, and 65% achieved at least a very good partial response (VGPR). No significant differences in the PFS were found between subgroups based on the maintenance following SAT (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.93, 95% CI: 0.48–1.8, p = 0.831), cytogenetic risk (standard vs. high-risk) (HR = 0.98, 95% CI: 0.49–1.99, p = 0.969), age (<60 years vs. ≥60 years) (HR = 0.96, 95% CI: 0.5–1.85, p = 0.912) or number of prior treatment lines (<3 vs. ≥3) (HR = 0.186, 95% CI: 0.95–3.61, p = 0.069). The duration of remission after the first ASCT did not influence the PFS or OS following SAT (HR = 1.63, 95% CI: 0.78–3.39, p = 0.193 and HR = 1.2, 95% CI: 0.46–3.09, p = 0.7130). Conclusions: Salvage autologous stem cell transplantation remains a viable treatment option for patients with relapsed MM, particularly in resource-limited countries or for patients who prefer short, fixed-duration therapy. However, as is known from previous studies, maintenance therapy is crucial for achieving longer PFS. In this study, no statistically significant factors were identified to predict the benefit, underscoring the need for further research to optimize patient selection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cutting-Edge Research in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma)
►▼
Show Figures
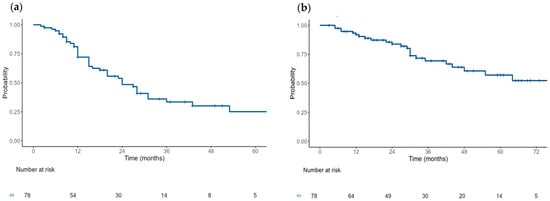
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Orthodontic Adhesives on the Subgingival Microbiota During Early Fixed Appliance Therapy: A Pilot Study
by
Krisztina Martha, Esztella-Éva Kis, Izabella Éva Mureșan and Andrei Constantin Ioanovici
Medicina 2025, 61(5), 858; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050858 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The most common method for treating malocclusions today is fixed orthodontic therapy, during which brackets and tubes are bonded to the surface of the teeth, which makes oral hygiene difficult to maintain. Increased plaque retention, gingival bleeding, and gingivitis
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The most common method for treating malocclusions today is fixed orthodontic therapy, during which brackets and tubes are bonded to the surface of the teeth, which makes oral hygiene difficult to maintain. Increased plaque retention, gingival bleeding, and gingivitis can be diagnosed in the early phases of treatment. The periodontal response to plaque accumulation can be explained by quantitative and qualitative changes in the subgingival microbiota. The aim of our research was to investigate the changes in the subgingival microbiota that occurred within 6–8 weeks after bonding when two different orthodontic adhesives were used. Materials and Methods: Thirty patients were followed; molar tubes were bonded with a composite (C) in fifteen cases, and in the other fifteen cases, they were bonded with glass ionomer cementum (GIC). A microbiological sample was taken from the gingival sulcus of the maxillary first molars at the time of appliance placement (T1) and 6–8 weeks (T2) after bonding. Bacterial DNA detection was performed using the micro-IDent®plus11 (Hain Lifescience GmbH, Germany) PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method. The statistical analysis included McNemar’s test to analyze the paired binary data and Fisher’s Exact Test to compare the prevalence of each of the 11 bacteria at T1 and, ultimately, T2 between the two studied groups. The Bonferroni correction was also applied. Results: When analyzing GIC vs. C at T1 and T2, none of the studied pathogens showed significant differences. Conclusions: Given the lack of statistical significance, these trends do not confirm a definitive impact of the procedure on bacterial presence. The increased presence of periodontal pathogens might suggest that bonding does not reduce the bacterial loading of subgingival microbiota. Less protective effects of the GIC intervention against Tannerella forsythia and Eubacterium nodatum bacteria were detected.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oral Physiology: Protective Mechanisms, Immune Responses and Pathways of Inflammation in Periodontal Conditions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Medicina Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
JCM, JPM, Medicina, Osteology, Surgeries
Orthopaedic Diseases and Innovative Intervention Strategies, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Umile Giuseppe Longo, Vicenzo DenaroDeadline: 31 May 2025
Topic in
Cancers, Healthcare, JCM, JPM, Medicina
Public Health and Healthcare in the Context of Big Data
Topic Editors: Mingzhe Ma, Xi Yang, Ruogu QiDeadline: 5 July 2025
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, JCM, Medicina, Onco
Cancer Biology and Radiation Therapy: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Chang Ming Charlie Ma, Ka Yu Tse, Ming-Yii Huang, Mukund SeshadriDeadline: 16 October 2025
Topic in
Clinics and Practice, Cosmetics, JCM, Medicina, Dermato, LabMed, Psychology International
Advances in Psychodermatology
Topic Editors: Jacek C Szepietowski, Andrzej JaworekDeadline: 30 November 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Medicina
Advances in the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Guest Editor: Emdio ScarpelliniDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Early Detection and Clinical Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury
Guest Editor: Yu-Jang SuDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Chronic Respiratory Diseases: Updates on Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Guest Editors: Marcin Kurowski, Laura Malinauskienė, Corrado PelaiaDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Advances and Challenges in Stroke Rehabilitation
Guest Editors: Trinidad Sentandreu-Mañó, José Manuel Tomás MiguelDeadline: 15 May 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Advances in Cornea, Cataract, and Refractive Surgery
Collection Editor: Ivo Guber
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interdisciplinary Medicine – The Key For Personalized Medicine
Collection Editor: Camelia Diaconu
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Pain, Bleeding, Trauma and Infections: The 4 Horsemen of the Apocalypse for the Emergency Medicine
Collection Editor: Marcello Candelli
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Frontiers in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Jimmy T. Efird, Tithi Biswas










